Engines
The Diesel Engine
The Diesel Engine
ENGINE RESOURSES
ENGINE POWER
FUEL CONSUMPTION
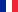
This is a modern diesel engine featuring the world latest engineering trends. Engine power - 149.6 h.p.
The Gasoline Engine
The Gasoline Engine
ENGINE RESOURSES
ENGINE POWER
FUEL CONSUMPTION
The gasoline engine. Euro-V emission standards.
The CNG/LPG Engine
The CNG/LPG Engine
ENGINE RESOURSES
ENGINE POWER
FUEL CONSUMPTION
The gasoline engine combined with original CNG/LPG kits can save you up to 200,000 RUR annually on fuel expenses. Fulfillment of Euro-4 standard.
|

|

|
|
THE DIESEL ENGINE |
THE GASOLINE ENGINE |
THE CNG/LPG ENGINE (PROPANE) |
|
Engine type |
Diesel, turbocharged and aftercooled engine |
Gasoline, |
Bi-fuel, 4-stroke, injection-type (gasoline/ gas) |
|
Number of cylinders and their arrangement |
4, in-line |
4, in-line |
4, in-line |
|
Diameter of cylinders and piston stroke, mm |
94×100 |
96.5×92 |
96.5×92 |
|
Cylinder capability, l |
2.8 |
2.69 |
2.69 |
|
Compression ratio |
16.5 |
10 |
10 |
|
Rated net power, KW (hp) at crankshaft rotation speed, rpm |
88.3 (120) 3600 |
78.5 (106.8) 4000 |
78.5 (106.8) for gasoline; 76.7 (104.3) for gas 4000 |
|
Peak net torque, N·m (kgf·m) at crankshaft rotation speed, rpm |
270 (27.5) 1400-3000 |
220.5 (22.5) 2350±150 |
220.5 (22.5) for gasoline; 219 (22.3) for gas 2350±150 |
|
Firing sequence |
1-3-4-2 |
1-2-4-3 |
1-2-4-3 |
|
Crankshaft rotation speed in idle mode, rpm minimum increase |
750±50 4500 |
800±50 3000 |
800±50 3000 |
|
Crankshaft rotation direction |
Right-hand |
Right-hand rotation |
Right-hand |
|
Distance to empty based on one fueling, for various fuel types |
475 |
— |
870 |
|
ECB |
one |
— |
common |
|
Total volume capacity of gas cylinder system, cubic m/kg |
— |
— |
80/96 |
|
Reference fuel consumption at constant speed: 60 km/h, l/100 km 80 km/h, l/100 km |
8.5 10.3 |
9.8 12.1 |
— — |
|
Reference gas consumption at constant speed: 60 km/h, cubic m/kg 80 km/h, cubic m/kg |
— — |
— — |
11.8 14.5 |